Table of contents
Hydrogen, the universe's most abundant element, is making waves as a clean energy source for a sustainable future.
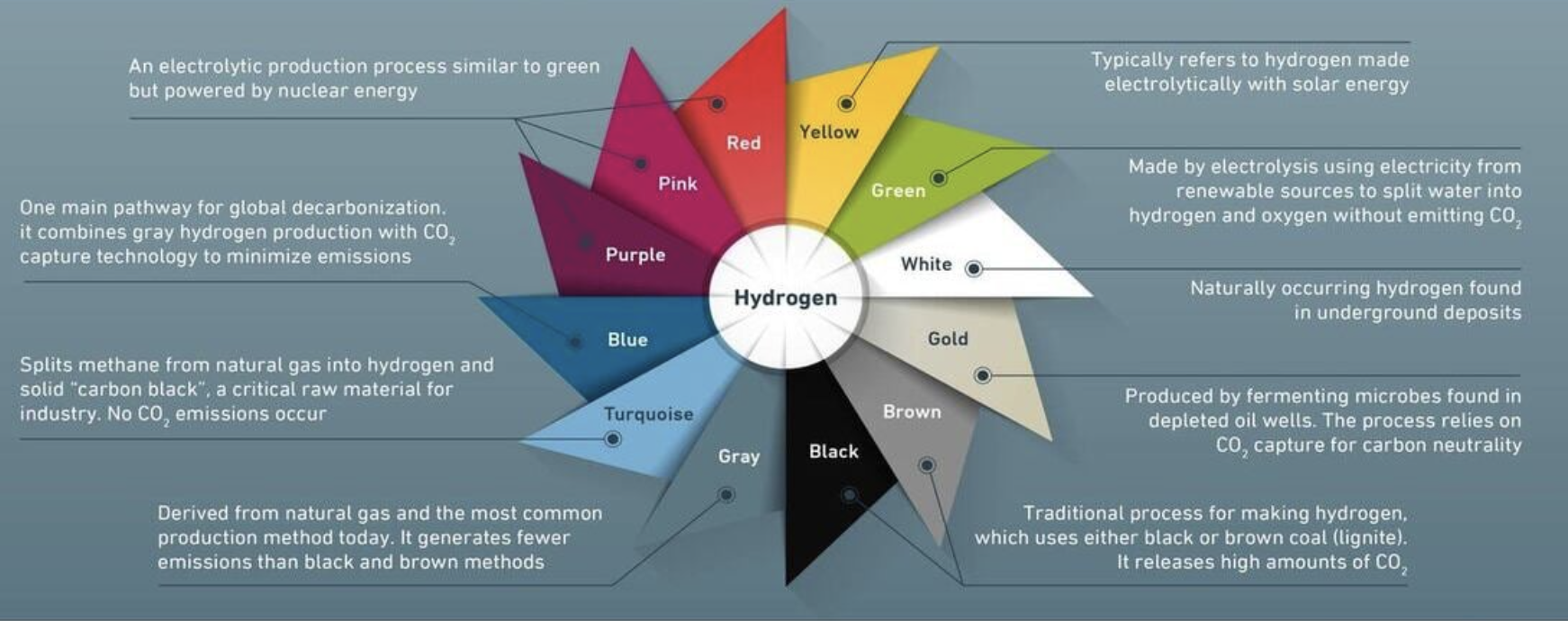
But did you know hydrogen itself comes in various colors? Understanding these color codes is crucial for UPSC aspirants to stay ahead of the curve in the energy sector. This article explains the different types of Hydrogens.
![Hydrogen color spectrum and indications for carbon emissions [11]. | Download Scientific Diagram](https://www.researchgate.net/publication/358515834/figure/fig1/AS:1122777025253376@1644702311974/The-hydrogen-color-spectrum-and-indications-for-carbon-emissions-11.png)
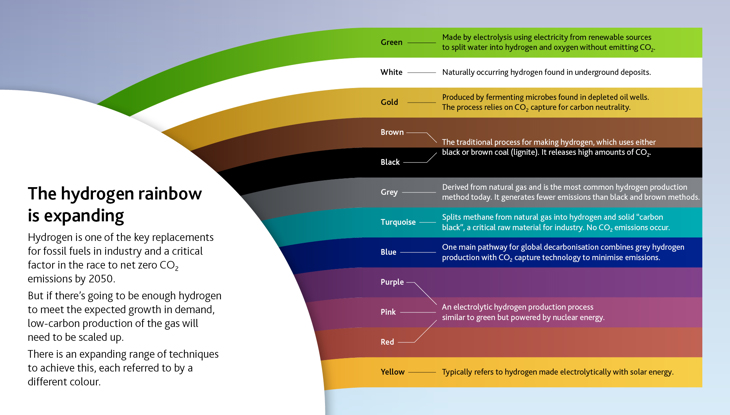
Green Hydrogen
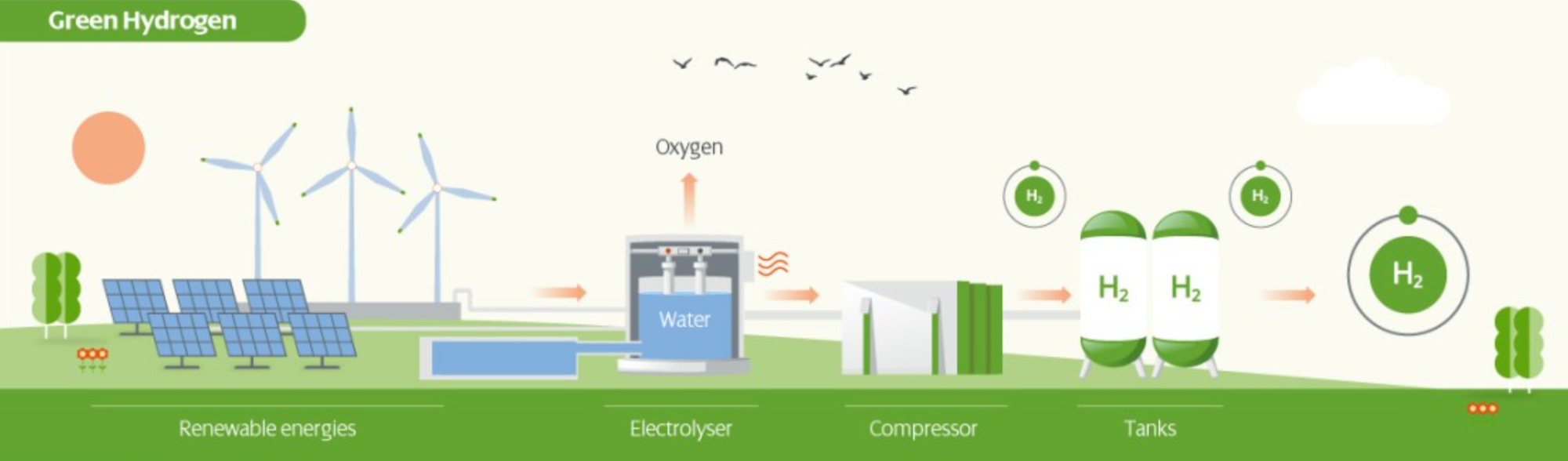
- Green hydrogen is created by use of renewable energy sources such as solar or wind which generates clean electricity for electrolysis of water.
- The electrochemical reaction splits water into its constituents hydrogen and oxygen, while producing no carbon dioxide.
- Green hydrogen has a high cost of generation due to it accounts for a small percentage in total hydrogen production.
Blue Hydrogen
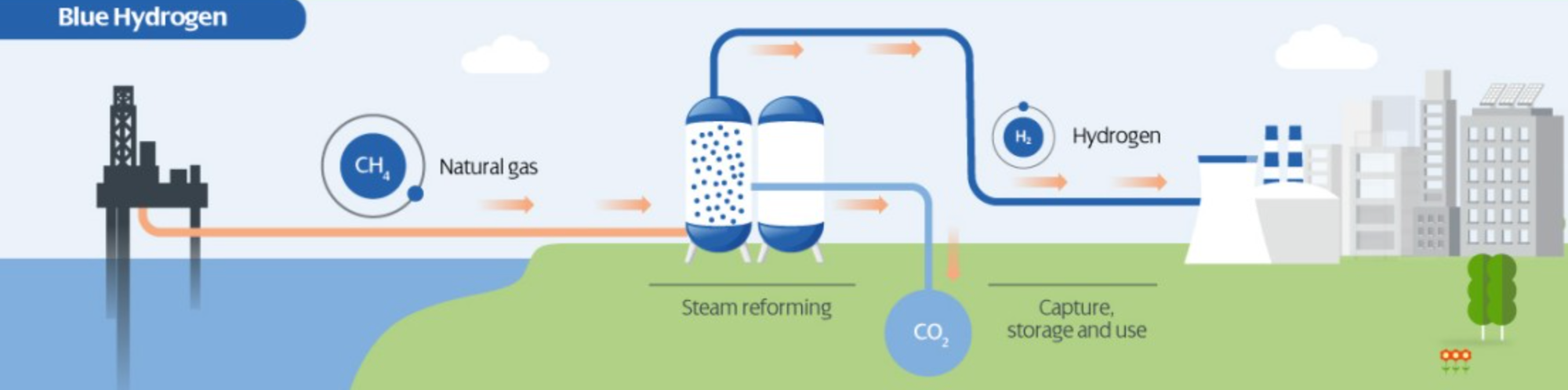
- Blue hydrogen is produced from natural gas by a process called steam reforming in0 which natural gas is combined with heated water in the form of steam.
- It results in formation of hydrogen but carbon dioxide is also produced as a byproduct.
- Therefore, the technique of carbon capture and storage is used to collect and store this carbon.
- Blue hydrogen is also called 'low-carbon hydrogen’ as there is slight production of greenhouse gasses.
Turquoise Hydrogen
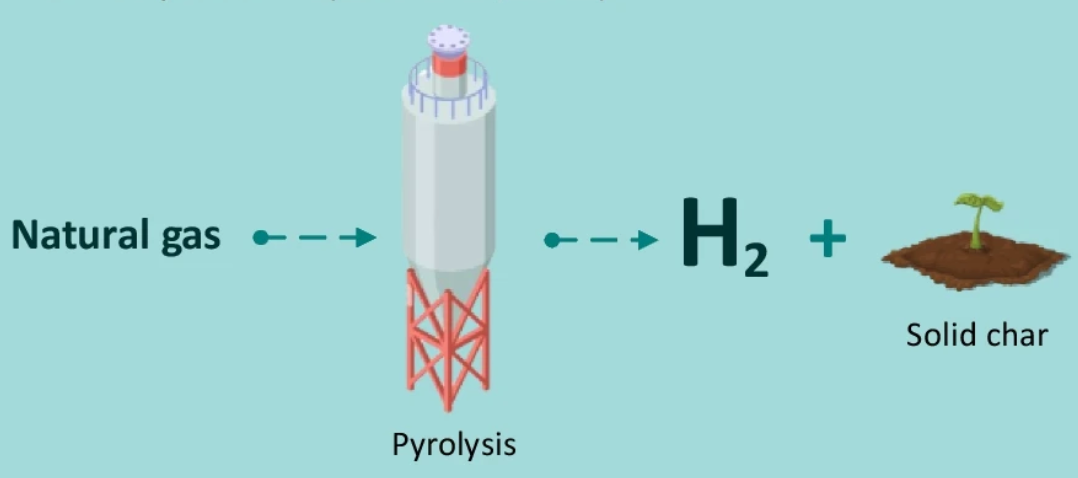
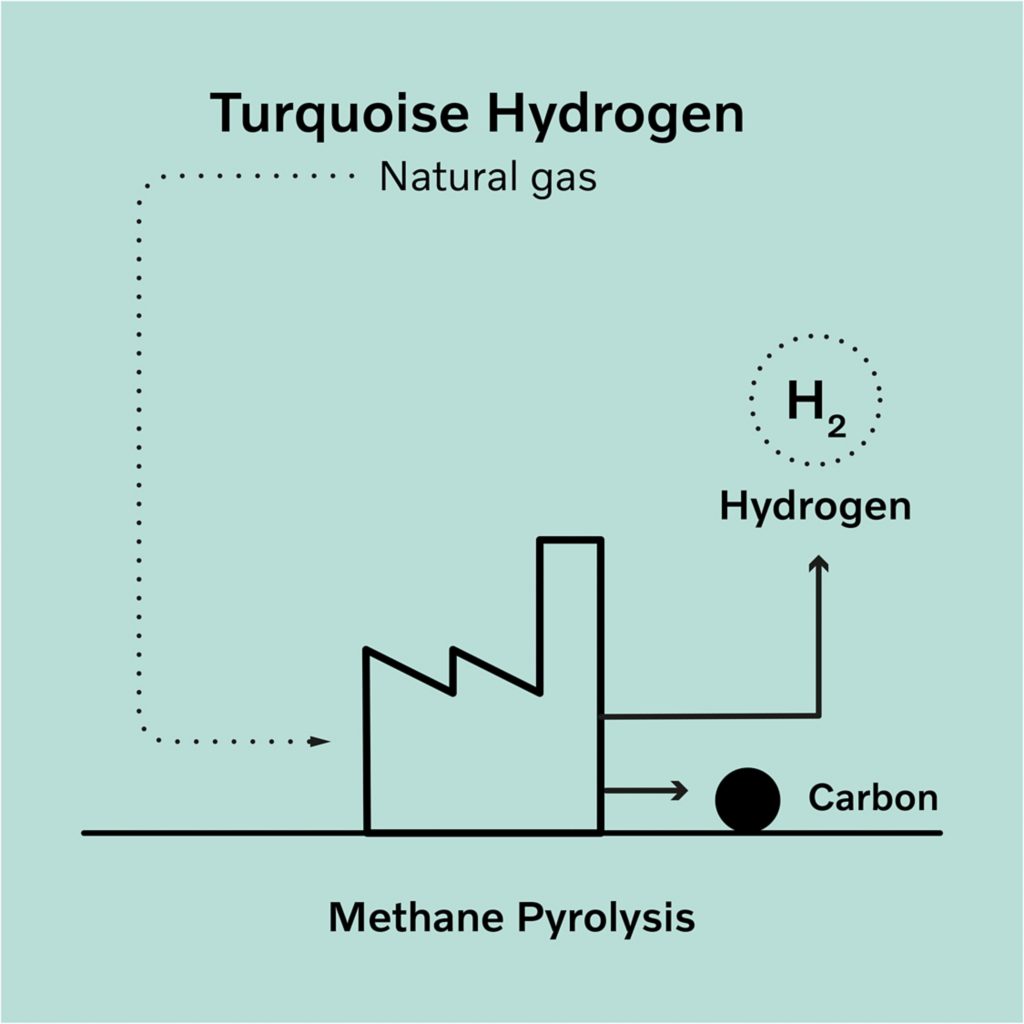
- This is a new type of hydrogen produced in the lab, and its commercial production has yet not started.
- It is produced by methane pyrolysis in which the end products are hydrogen and solid carbon.
- It is a low-emission hydrogen because the heating process is fueled by renewable energy and the carbon is permanently stored or utilized.
Grey Hydrogen
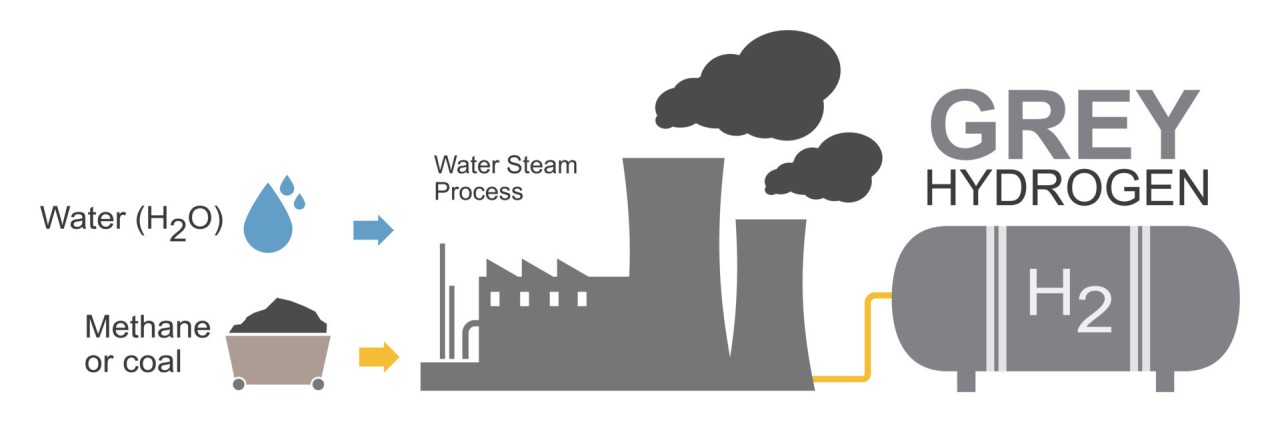
- Grey hydrogen is produced by the process of steam methane reformation by using natural gas or methane.
- It is not eco friendly because greenhouse gasses are produced but it is the most popular method of producing hydrogen.
- This method of hydrogen production does not involve carbon capture and storage.

Black and Brown Hydrogen
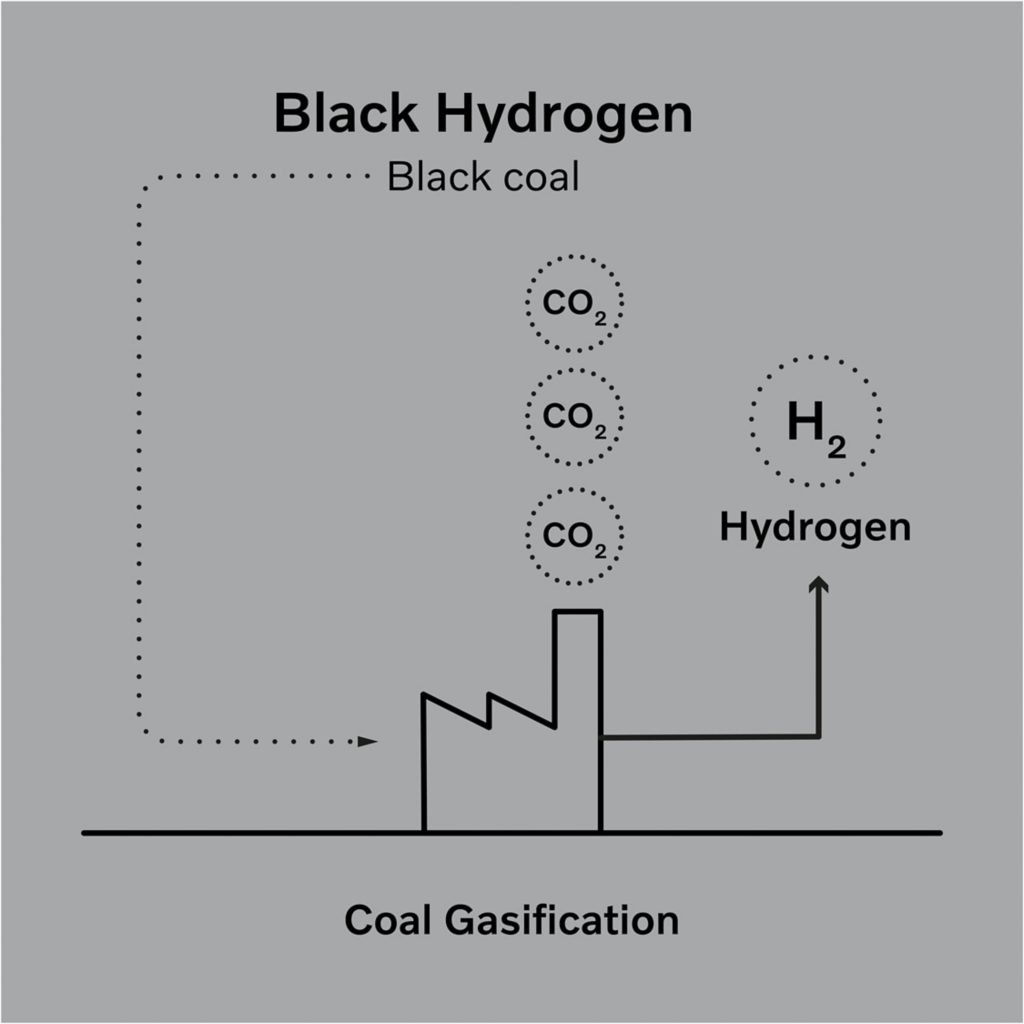
- This method is more harmful ecologically as compared to Grey hydrogen production as there is usage of black coal or lignite.
- Also, both the carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide generated during the process are not recaptured.
- Cost comparison of types of hydrogen reveals ecologically beneficial hydrogen to be costlier.
- A kilogram of black hydrogen costs USD 0.9-1.5 while gray hydrogen costs USD 1.7-2.3, blue hydrogen costs from USD 1.3-3.6 and green hydrogen costs USD 3.5-5.5 per kg.
Pink Hydrogen
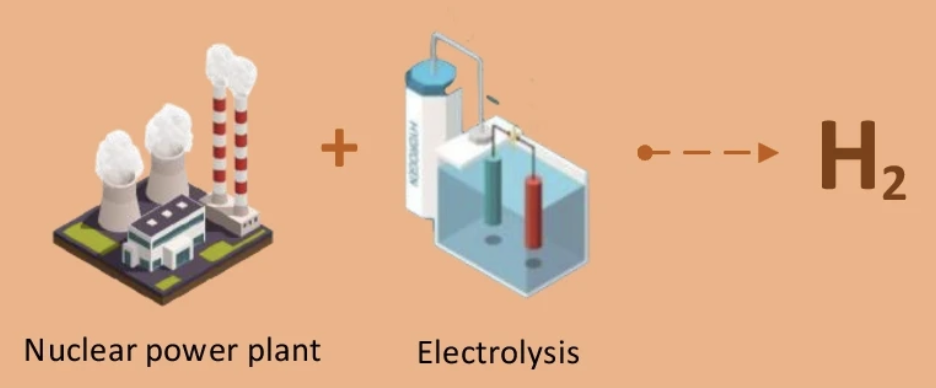
- Pink hydrogen is produced by a nuclear-powered electrolysis process and it is also called purple or crimson hydrogen.
- The high temperatures produced by nuclear reactions can be used to produce steam for better electrolysis or steam methane reformation.
Yellow Hydrogen
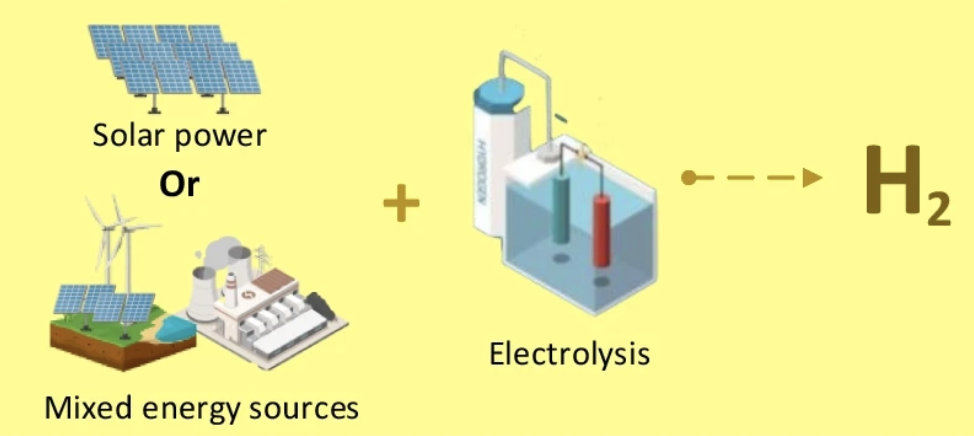
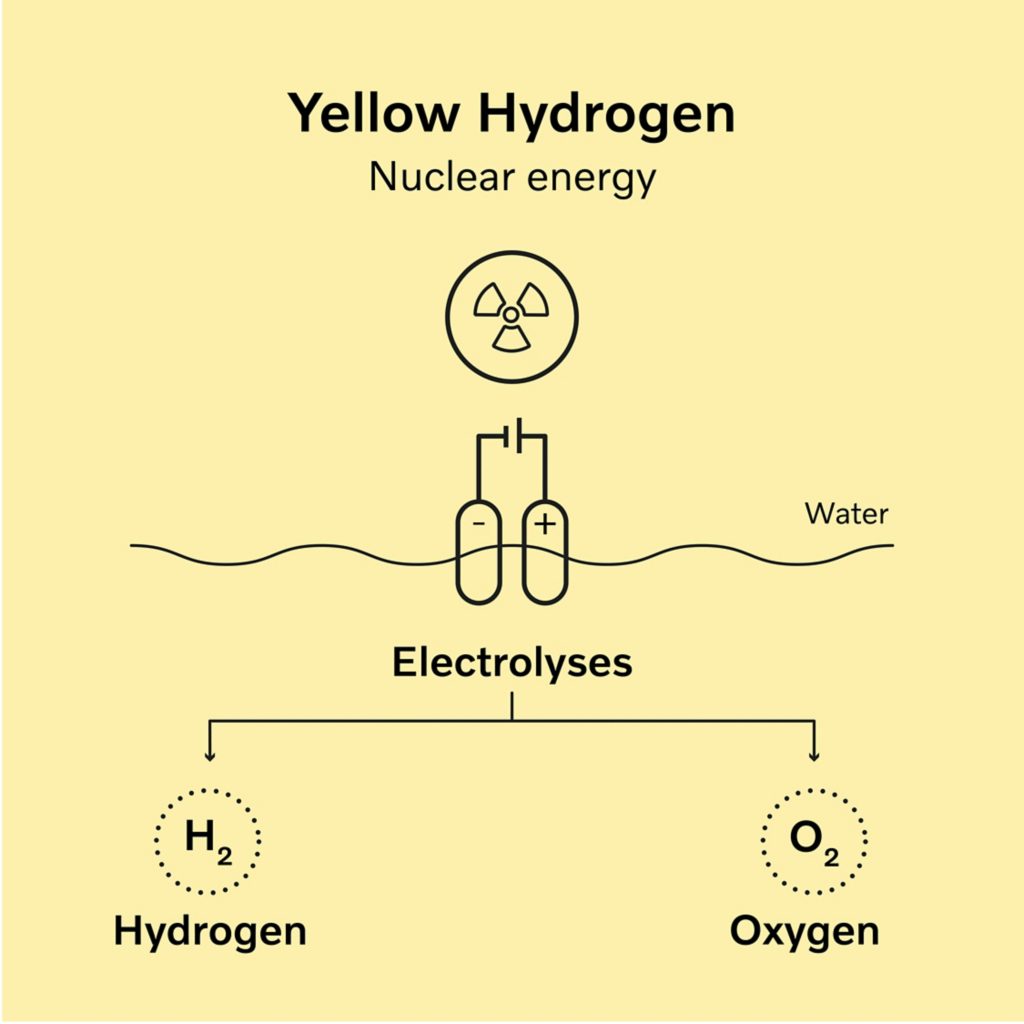
- Yellow hydrogen is a type of hydrogen produced by solar-powered electrolysis.
- However, it is also used to describe electrolyzed hydrogen produced using a combination of renewable and fossil fuel power.
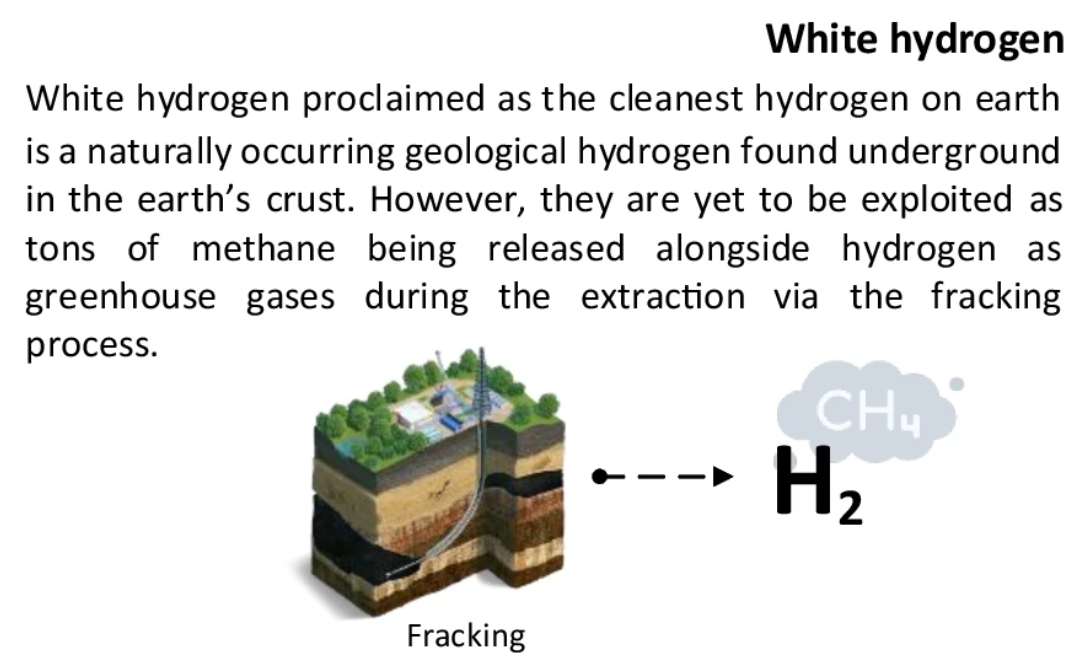
White Hydrogen
- Also called natural or geologic hydrogen, white hydrogen is not produced but it is a naturally occurring hydrogen type found in subsurface deposits.
- These deposits are easily accessible by drilling a well.
- Mali, Brazil, Australia, and other countries are actively extracting white hydrogen.
- Natural processes which contribute to the formation of white hydrogen include degassing from the Earth's crust and mantle, reactions with rocks, and interactions with water and minerals.
Gold Hydrogen

- Gold hydrogen is a new type of hydrogen created by fermenting bacteria mostly found in depleted oil wells.
- This is a low-cost hydrogen extraction method which has added benefits of extending the life of oil fields.
- Its synthesis and extraction process relies on carbon dioxide collection.
Summary: Hydrogen Colorwheel